 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
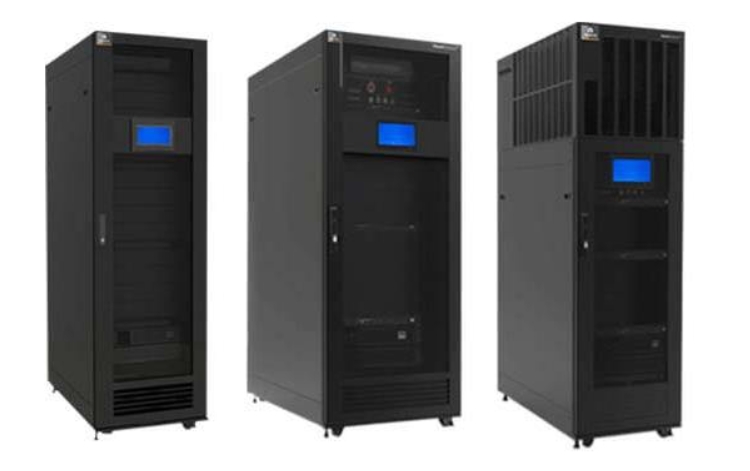

RFID smart cabinet refers to a reader-writer in the form of a cabinet, which is a type of fixed reader-writer. Because in recent years, a number of RFID smart cabinet players have emerged on the market. This type of product is also an industry a new growth point In terms of technology types, RFID smart cabinets mainly include two frequency bands: UHF and HF. Many smart cabinets will integrate UHF and HF capabilities. This report mainly focuses on UHF cabinets. HF smart cabinets have been commercialized earlier, especially in the field of books and archives, and are widely used. However, in recent years, UHF smart cabinets are increasing rapidly. At present, the proportion of UHF and HF cabinet products is relatively close. In recent years, RFID smart cabinets have been a bright spot in the industry. There are two main reasons. The first aspect is that the market for smart cabinets is growing rapidly, including medical, library and archives, finance, industry and other fields. For RFID smart cabinets, The demand is growing rapidly. The second aspect is that the price of smart cabinets is high and the profits are relatively good. A simple understanding of a smart cabinet is a product that combines a traditional cabinet with an RFID reader. Therefore, manufacturers of smart cabinets need to have two parts. One is the sheet metal part.It is usually outsourced, but some manufacturers do it themselves; the other part is the RFID reader part, which is the RFID manufacturer's own advantage.

Handheld (Including tablet, Handheld devices,wearable devices, etc.) refers to mobile, portable UHF RFID reader devices, of which handheld is the most common form. This type of product is characterized by lightweight, easy to move in real time, and the handheld machine can be understood as a mobile phone with UHF RFID function, in addition to RFID identification In addition to reading, it also has most functions of ordinary mobile phones, which is very suitable for storage inventory, asset management, personnel behavior management and other applications. UHF RFID mobile phone have high degree of standardization, lightweight and portable characteristics, so it's more suitable for consumer applications, once the volume, it has a high Imagination space. In the current market environment, handheld devices are mainly used in B-end scenarios such as logistics, finance, retail, and industry, and B-end scenarios are characterized by slow start, except in certain scenarios There are policies to push, so we believe that in the current market environment, the growth of handheld device shipments in the B-side scenario and the growth of the entire reader market,The degree is basically the same. One of the biggest variables in the mobile phone market is the express logistics market, and once the application of express logistics breaks out, the demand for UHF RFID mobile phones is well known.Because the market is still in the early validation stage, so when we evaluate expectations, we eliminate this factor, and we will also monitor the industry in real time Above are the latest developments, there are certain information will be updated in time.
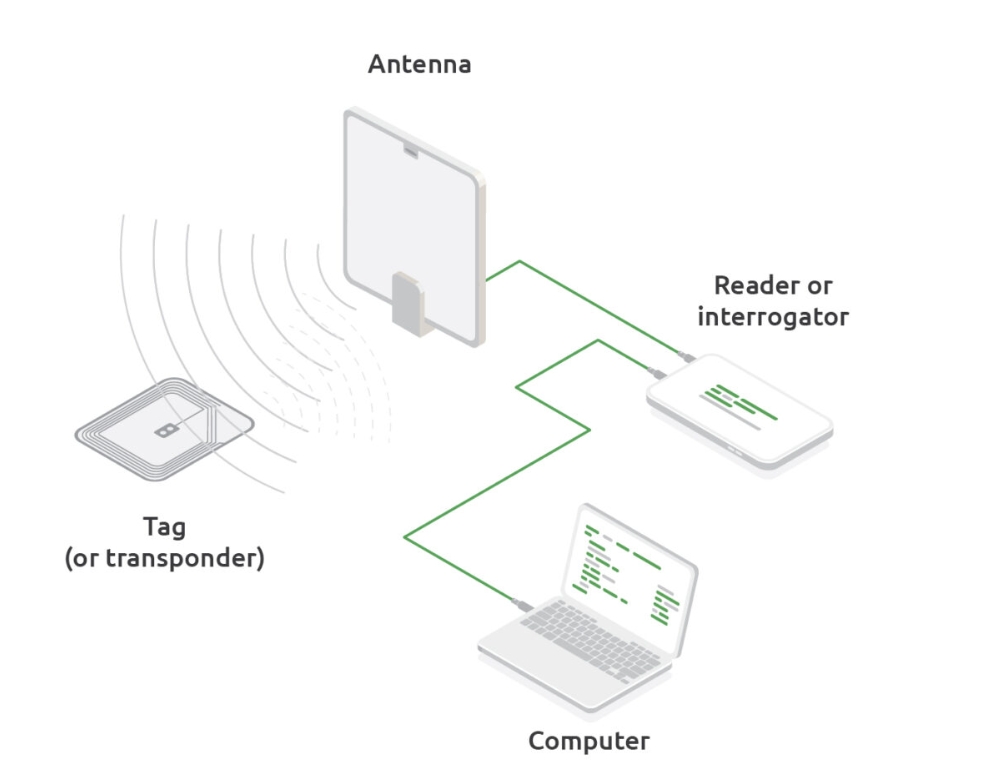
UHF RFID reader terminals come in various forms. Depending on the application scenarios, the final terminal forms are different. In the industry, readers are generally classified based on whether they are in a fixed position or can be moved when used. They are divided into two categories: Fixed readers and Mobile readers. In this survey, based on market popularity, we selected large-volume and relatively high-priced products such as printers, smart cabinets, and channel reader from fixed readers for separate analysis. The specific categories are: • Handheld devices (Including other portable reader/writer devices). Among this type of products, the most important form is handheld devices. In addition, there are also some tablets and wearable products. When applied to the market, they are all classified into the same category. • Printer is a common form of RFID fixed reader and writer. It is mostly used for printing white label cards. Or the application terminal performs a small amount of re-labeling due to label loss. Or scenarios such as logistics, finance, electricity, and medical care where the number of tags is relatively small and the degree of customization is high. • Channel reader is a form of fixed reader that uses bayonet ports for warehouse entry and exit management and asset management. • Smart cabinet is a recently developed fixed reader-writer product, mostly used for asset management. • Other fixed reader/writer equipment:Excluding fixed reader/writer products other than smart cabinets, printers, and channel readers, including all-in-one machines, card issuers, and gateways Readers and writers, desktop readers and writers, cashier equipment, testing equipment, experimental equipment, etc. • Discrete device readers and writers refer to UHF RFID readers and writers built with discrete devices. They do not use standard chips. In some scenarios, such products can customized according to user needs. Especially recently, some large projects on the market have adopted this type of products,The products are available in various forms, both fixed and removable.

In the fast-paced hospitality and healthcare industries, efficient linen management is essential to ensure seamless operations and exceptional guest experiences. Traditional manual tracking methods often result in inaccuracies, lost items, and increased labor costs. However, with the emergence of revolutionary RFID laundry tags, linen management is undergoing a transformative shift. UHF RFID antenna technology plays a vital role in the effectiveness of RFID laundry tags. These antennas are specifically designed to facilitate long-range communication between the RFID tags and readers, enabling seamless tracking and identification of linens throughout their lifecycle. One of the key advantages of UHF RFID antenna technology is its ability to achieve long-range communication. With a properly installed and optimized UHF RFID reader antenna, linen tracking can be performed with great accuracy and efficiency. This means that linens can be automatically identified and counted from a distance, eliminating the need for manual sorting and reducing labor costs. Furthermore, the UHF RFID reader antenna allows for improved read rates, even in challenging environments such as crowded linen storage areas or busy laundry facilities. This ensures accurate and reliable data capture, preventing errors and ensuring that linens are properly managed and accounted for. Manufacturers of UHF RFID antennas play a crucial role in the development and supply of these cutting-edge technologies. They utilize rigorous testing and advanced engineering techniques to produce high-quality antennas that deliver exceptional performance. By partnering with reliable UHF antenna manufacturers, hospitality and healthcare organizations can access antennas that are specifically designed to meet their unique linen management requirements. When integrating UHF RFID antenna technology into linen management systems, it is essential to consider the size and form factor of the antennas. In the case of laundry facilities, where space is often limited, small UHF RFID antennas are highly desirable. These compact antennas can be discreetly installed in various areas, such as laundry carts, storage shelves, or conveyor systems, without occupying excessive space. With the integration of UHF RFID antenna technology into linen management systems, several benefits are realized. First and foremost, the accurate and real-time tracking of linens significantly reduces losses and minimizes the need for frequent replacements, leading to substantial cost savings for hospitality and healthcare establishments. Moreover, the automation of linen management processes reduces human error, ensures efficient distribution, and enhances overall guest satisfaction. Linens can be precisely tracked from acquisition to storage, and even during laundering, enabling proactive inventory management, timely replacements, and enhanced quality control. This, in turn, promotes a seamless guest experience, as linens are readily avail...
Introduction: RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has found wide-ranging applications in various industries, offering efficient tracking and management solutions. In this article, we will explore the application layer of RFID readers, focusing on the utilization methods and providing illustrative examples of their practical implementations across different sectors. Utilizing RFID Laundry Tags: RFID laundry tags have become invaluable in the textile and hospitality industries, where efficient management of linens and garments is essential. These tags are designed to withstand harsh washing and drying conditions, ensuring their longevity. By affixing washable RFID tags to each item, hotels, hospitals, and laundries can automate their inventory processes, track item location, and optimize resource allocation. Leveraging Long-range UHF RFID Tags: Long-range UHF RFID tags find applications in large-scale asset tracking and inventory management. With an extended read range, these tags enable rapid and accurate scanning of items from a distance. For instance, in a warehouse setting, utilizing long-range UHF RFID tags on pallets or containers allows for quick identification and efficient stock management, minimizing errors and maximizing operational efficiency. Exploring UHF RFID Stickers: UHF RFID stickers are compact, adhesive labels that provide convenience and versatility in tracking various objects. These stickers can be easily attached to assets, products, or containers, enabling automatic identification and data capture throughout the supply chain. Retailers can utilize UHF RFID stickers on individual items to streamline inventory management, reduce stockouts, and improve overall store operations. Considerations for UHF RFID Tag Pricing: The cost of UHF RFID tags varies based on factors such as functionality, read range, durability, and volume. Different suppliers and manufacturers offer a range of options, allowing businesses to select tags that align with their budget and specific requirements. Price considerations should also account for the long-term benefits gained through improved inventory accuracy, enhanced theft prevention, and streamlined logistics processes. Implementing UHF Anti-Metal Tags: UHF anti-metal tags are specifically designed to overcome the challenges posed by metallic surfaces. These tags feature specialized shielding technology, allowing them to be attached to metal objects and still maintain accurate read rates. Industries such as manufacturing, construction, and logistics can utilize UHF anti-metal tags to track metal assets, tools, or machinery, improving overall traceability and reducing loss or misplacement. Selecting Reliable RFID Tag Manufacturers and Suppliers: When procuring RFID tags, it is essential to choose reputable manufacturers or suppliers. These entities ensure product quality, customization options, and ongoing technical support. RFID tag manufacturers and suppliers, with their expertise and...

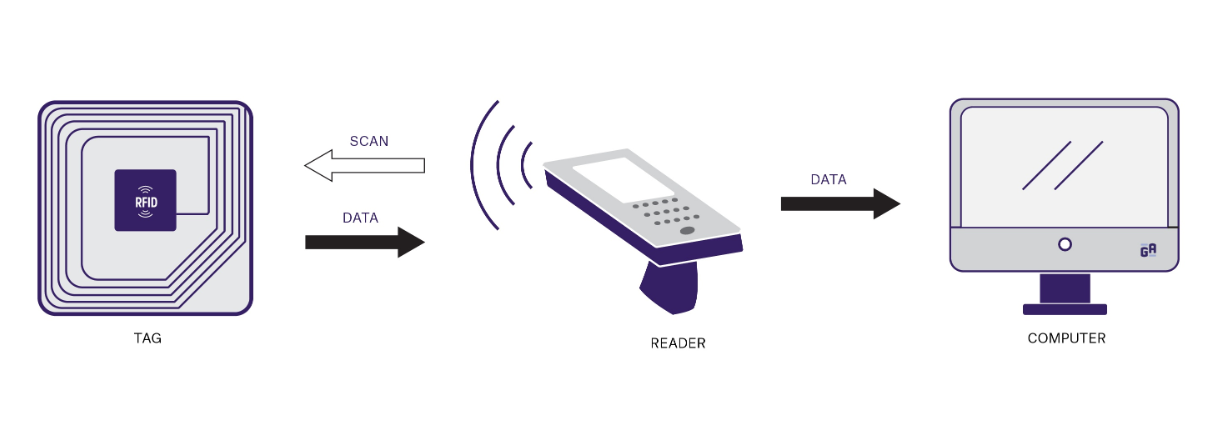
Intelligent transportation systems are a crucial component of modern urban traffic management, where RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology plays a significant role. The working principles and application scenarios of RFID readers in intelligent transportation, particularly within vehicular networks, are gaining increasing attention. 1. Overview of RFID Technology RFID technology is a wireless communication technology that automatically identifies targets and retrieves related data using radio waves. It mainly consists of RFID tags (or cards) and RFID readers (or interrogators). RFID tags are installed on objects to be identified, while RFID readers are responsible for reading and writing data to tags. 2. Working Principles of RFID Readers The working principles of RFID readers can be simplified into three steps: Signal Emission: RFID readers emit radio frequency signals. Response Reception: When an RFID tag enters the reader's detection range, the tag receives the emitted signal. Data Transmission: Upon receiving the signal, the RFID tag extracts energy and activates the circuitry inside the tag, then transmits the stored information back to the reader via radio waves, completing the data retrieval process. 3. Applications of RFID Readers in Intelligent Transportation In intelligent transportation systems, the applications of RFID readers can be seen in several areas: Vehicle Identification and Management: RFID technology is used for automatic vehicle identification and management, such as in Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) systems. By installing RFID tags on vehicles, RFID readers can automatically read vehicle information, enabling cashless payments and fast passage. Traffic Flow Management: RFID readers can be installed at traffic junctions or highway entrances to monitor real-time vehicle flow, providing traffic management authorities with real-time traffic information to optimize traffic flow. Smart Parking Management: In parking management, RFID technology can be used to identify and manage parked vehicles, improving parking lot utilization and security. Drivers can use RFID-tagged cards or tags installed on their vehicles for automated recording of vehicle information and parking duration, facilitating unmanned parking management. Vehicle Security and Anti-theft: RFID technology enables vehicle identification and theft prevention. With RFID tags installed, the system can track the vehicle's location and status in real time. If a vehicle is stolen, the RFID system can quickly locate and track it. 4. Future Prospects As intelligent transportation technology continues to develop, RFID technology's application in vehicular networks has significant potential for growth. As RFID technology matures and costs decrease, RFID readers will become more ubiquitous, with broader application scenarios, thereby providing more possibilities for the development of intelligent transportation systems. In conclusion, RFID readers, as...
Introduction: RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has undergone significant advancements, resulting in the development of diverse RFID readers and tags to meet the evolving needs of different industries. In this article, we will discuss the changes in RFID tags and readers, their associated costs, usage methods, and provide illustrative examples of their applications in practical scenarios. Evolution of RFID Readers: The advent of 2.4 GHz RFID readers has brought about notable improvements in communication and data processing speeds. These readers operate at higher frequencies, enabling faster and more reliable data transmission. Moreover, long-range RFID readers have emerged, extending the reading distance and enhancing scalability in various environments. These advancements have revolutionized industries by enabling efficient inventory management and asset tracking across large areas, such as warehouses, distribution centers, and industrial facilities. RFID Reader Manufacturers and Suppliers: Numerous companies specialize in manufacturing RFID readers, ensuring a diverse range of options to cater to specific business requirements. From established manufacturers with a global presence to smaller suppliers, businesses have access to quality RFID reader solutions. Selecting the right manufacturer or supplier is crucial as it ensures product reliability, compatibility, and ongoing technical support. Cost Considerations: The cost of RFID readers varies based on factors such as features, capabilities, read range, and brand. Long-range RFID readers, designed for extended read distances, often entail a higher price point compared to standard range readers. Additionally, active RFID readers, which operate with active RFID tags, usually involve higher upfront costs due to their advanced functionality. However, the benefits they provide, such as real-time tracking, increased accuracy, and improved operational efficiency, may outweigh the initial investment. Practical Applications and Usage Methods: Long-range RFID scanners find applications in diverse sectors. For instance, in the logistics industry, these scanners streamline the tracking and tracing of goods, enabling efficient supply chain management. In retail, long-distance RFID card readers facilitate secure access control and convenient customer experiences, allowing quick identification and authorization for entry. In healthcare, long-range RFID tag readers assist in equipment management, ensuring timely maintenance and reducing downtime. Examples of Active RFID Reader Applications: Active RFID readers, when used in conjunction with active RFID tags, deliver enhanced capabilities for real-time tracking and monitoring. Industries such as oil and gas, mining, and construction rely on active RFID readers to monitor valuable assets across expansive and rugged areas. These readers enable remote monitoring of equipment, personnel tracking for safety purposes, and efficient inventory manageme...
Introduction: RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has revolutionized the way businesses operate across different industries. Among its many variations, active RFID tags have gained significant popularity due to their enhanced capabilities. These tags contain an internal power source, allowing them to transmit information to RFID readers over long distances. In this article, we will explore the diverse applications of active RFID tags and readers in different practical scenarios. Supply Chain and Logistics: Active RFID tags have become a vital component in managing supply chains and logistics operations. They enable real-time tracking of goods, optimizing inventory management, and improving overall efficiency. For instance, in a large warehouse, active RFID tags can be attached to pallets or containers, allowing automated monitoring of inventory levels and facilitating accurate and timely restocking. Asset Tracking: Active RFID tags are extensively used for asset tracking in industries such as healthcare and manufacturing. By attaching tags to valuable assets like equipment, tools, or vehicles, organizations can ensure their proper utilization and timely maintenance. Hospitals employ active RFID tags to track medical equipment, reducing time wasted searching for specific items and improving patient care. Security and Access Control: The active UHF RFID tags play a crucial role in secure access control systems. These tags can communicate with readers from a significant distance, making them suitable for applications such as parking facilities, gated communities, and restricted areas. By utilizing active RFID technology, organizations can enhance security measures and streamline access procedures, effectively managing personnel and visitor access. Livestock Management: Active RFID tags find practical application in livestock management. Farmers can attach these tags to animals, allowing for accurate monitoring of their movements and overall health. Sensors on the tags can collect and transmit animal-related parameters such as temperature, location, and behavior to the readers. This data enables farmers to make informed decisions regarding animal health, breeding patterns, and grazing areas. Retail and Inventory Management: The retail industry benefits from active RFID tags for efficient inventory management and loss prevention. By affixing tags to individual products or product categories, retailers can monitor stock levels, prevent theft, and automate the inventory replenishment process. Additionally, active RFID readers placed at store exits can trigger alarms if unpaid items with active tags leave the premises, reducing shrinkage and enhancing store security. Conclusion: Active RFID tags and readers have proved their worth in a wide range of practical situations, offering increased efficiency, improved asset tracking, enhanced security, and streamlined operations across various industries. Whether it's managing supply chains, trackin...
Categories
New Products
JT-6210 0-1m UHF RFID Desktop USB Reader Writer ISO18000-6C Read More
JT-7100 0-3m 860-960MHz UHF RFID Industrial Grade RFID Reader Read More
JT-8380 0-6m UHF RFID 860-960MHz Middle Range Integrated Reader Read More
JT-P983 Industrial Tablet Pad RFID Handheld Reader Grade Long Range Android UHF Terminal Bluetooth RFID Reader For Warehouse Read More
JT-1550 Small Mini HF RFID 13.56MHz Module ISO14443A ISO 15693 Protocol Read More
JT-2302A 13.56MHz RFID Module ISO14443A ISO15693 Protocol Read More
JT-2302 HF RFID 13.56MHz Module ISO14443A ISO15693 Support Mifare1 IC card Read More
JT-2540 TM200 UHF RFID 4-port Module 860-960MHz TTL Read More
Copyright © 2026 Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

IPv6 network supported