 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com

As global urbanization continues to accelerate, land resources are becoming increasingly scarce, and ocean space is emerging as a new frontier for human expansion and development. From offshore wind power platforms and floating docks to future visions of floating cities, the concept of “offshore urban environments” is gradually becoming a reality. However, the marine environment is complex and dynamic, with dispersed infrastructure, difficult maintenance conditions, and highly mobile resources. Traditional management approaches struggle to meet the demands of efficient and refined operations. In this context, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), as a core component of the Internet of Things, is becoming a key enabler of offshore urban operating systems. Compared with traditional land-based cities, offshore urban systems face multiple operational challenges. Floating platforms and modular structures are widely distributed, making manual inspection costly and inefficient. Harsh environmental factors such as seawater corrosion, salt spray, and strong winds place higher demands on system stability and identification technologies. Meanwhile, material transport and personnel movement rely heavily on vessels or autonomous systems, making real-time monitoring more difficult. In the event of equipment failure or emergencies, rapid localization and response become critical. These challenges essentially stem from limited visibility and traceability—areas where RFID provides an effective solution. RFID establishes a comprehensive data acquisition network through tags, readers, and backend systems, enabling all assets within an offshore city to have unique digital identities. Floating building modules, energy equipment, vessels, emergency supplies, and personnel gear can all be tagged and managed. Technologies such as UHF RFID sticker solutions allow fast deployment across diverse surfaces, transforming isolated physical entities into interconnected digital nodes within a unified system. In practical operation, RFID systems continuously capture dynamic data on infrastructure and resources. By deploying readers at ports, storage areas, and key operational nodes—or integrating with autonomous inspection robots and unmanned vessels—the system can monitor equipment status, track material flows, and manage personnel distribution in real time. For example, directional RFID reader devices installed at docking points can automatically detect incoming shipments, enabling contactless receiving and real-time inventory updates while minimizing human error. With RFID-generated data, offshore city management can shift from reactive responses to proactive, data-driven decision-making. Systems can automatically trigger replenishment alerts based on inventory levels, schedule maintenance based on equipment usage, and optimize personnel and logistics routing. For instance, when a critical component approaches its maintenance cycle, the system can generate a task and assign t...
In the context of continuous digitalization and the evolution of the Internet of Things, the boundary between the physical world and the digital world is gradually blurring. In the past, humans relied on manual records and limited sensing methods to understand reality. Today, however, a data-driven “perception network” is taking shape. Within this network, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is no longer just a simple tagging tool—it is evolving into a critical node that connects the physical world with digital systems, functioning much like a “neural endpoint” that provides foundational sensing capabilities. In its early stages, RFID technology primarily addressed the problem of identification. By attaching electronic tags to objects and using readers for wireless communication, systems could quickly obtain identity information. This significantly improved efficiency, especially in logistics, warehousing, and retail, marking a shift from manual scanning to automated identification. At the hardware level, the integration of components such as the UHF RFID module has further standardized and miniaturized deployment, making large-scale adoption more practical. However, at this stage, RFID essentially remained a passive recording tool—it could answer “what is this,” but not “what condition is it in right now.” As application demands have grown, RFID has begun integrating with sensor technologies, gradually acquiring the ability to perceive environmental and status-related data. For instance, in cold chain logistics, RFID tags can incorporate temperature monitoring to record environmental changes in real time. In industrial manufacturing, RFID can be combined with equipment data to monitor operational status and production progress. Meanwhile, advances in infrastructure—such as the adoption of the long range RFID reader module—enable wider coverage and more flexible deployment across complex environments. This evolution signifies that RFID is no longer just a gateway for data input but has become an active participant in data generation—transforming from an identification tool into a sensing node. When RFID nodes are deployed at scale across physical spaces, a structure resembling a neural network begins to emerge. Each tag acts as a point of data collection, each reader as a channel for data transmission, and backend systems are responsible for integration and analysis. This architecture closely mirrors biological nervous systems: widely distributed, responsive in real time, and highly coordinated. In such a system, RFID is no longer an isolated device but a fundamental unit embedded within a broader intelligent network, enabling continuous perception of the physical world. At the application level, this “neuralized” RFID system is already being implemented across multiple industries. In smart logistics, RFID gives every item a traceable digital identity, recording every stage from production to delivery and forming a complete data chai...
In today’s rapidly advancing fields of life sciences, medical research, and biotechnology, life itself is being digitized at an unprecedented pace. From gene sequencing and cell culture to precision medicine and bioinformatics analysis, vast amounts of data are continuously generated, processed, and modeled. Yet behind these highly abstract digital achievements lies a fundamental reality: every algorithm and model ultimately originates from physical biological samples. If the identity of these samples cannot be accurately recognized and continuously tracked in the physical world, even the most advanced algorithms may be built on unreliable foundations. For a long time, biological sample management has relied on manual registration, paper labels, or barcode systems. While such approaches may be workable at small scales, their limitations become increasingly evident as sample volumes grow to tens or hundreds of thousands. Labels can be damaged, information can become fragmented, and manual operations are often difficult to audit. Once sample identities are compromised, the reliability of experimental data, analytical conclusions, and even scientific outcomes is inevitably affected. Against this backdrop, RFID technology has begun to enter the life sciences domain and is gradually becoming a foundational component of digital life management systems. By attaching a UHF RFID sticker to each biological sample container—such as cryogenic tubes, culture plates, or specimen vials—samples are endowed with a persistent digital identity. Unlike visual identifiers, RFID labels remain readable in low-temperature, sealed, or sterile environments, making them particularly suitable for laboratory and biobank applications. With the adoption of RFID, biological samples are no longer merely physical objects on laboratory benches; they become continuously mapped entities within digital systems. From collection and storage to transportation and experimental processing, every operation, location change, and status update can be automatically captured through industrial RFID reader infrastructure. These systems enable reliable batch reading and real-time monitoring without direct human intervention, forming a complete and verifiable lifecycle record for each sample. The true value of digital life management systems lies not only in improved operational efficiency, but also in their ability to provide reliable entry points for intelligent algorithms. In automated storage facilities or cold-chain environments, a long range RFID reader module can track large volumes of biological samples simultaneously, ensuring that physical movements are accurately synchronized with digital records. This allows artificial intelligence models to operate with confidence—knowing exactly which sample is being analyzed, under what conditions, and through which processes. At the algorithmic level, RFID-linked sample data can be deeply integrated with genomic information, clinical records, expe...

If one of the most profound transformations of the past two decades has been the digitalization of human identity—through ID cards, phone numbers, online accounts, and digital wallets—then the next two decades will witness a quieter but equally significant shift: machines are being systematically assigned identities of their own. As robots move beyond isolated tools and enter factories, warehouses, hospitals, city streets, and even homes—collaborating with humans and other machines—a fundamental question can no longer be avoided: how does a system know who a machine is? In human society, this question is answered by identity cards, passports, and social identification systems. In the emerging robotic society, that role is increasingly being played by RFID. A robot without a stable, verifiable identity can only be treated as a replaceable device. Once it is given a recognizable and traceable identity, however, it becomes part of a managed system—subject to rules, permissions, and responsibility. Identity is the line that separates tools from participants. In the early days of automation, robots did not need identities. A robotic arm performed fixed movements, an AGV followed predefined routes, and recognizing the individual machine was largely irrelevant. Today, this assumption no longer holds. Robot populations are growing rapidly, collaboration is becoming more complex, and robots are being deployed in open and semi-open environments. Systems must know which robot is executing a task, whether it is authorized to enter a restricted area, and who—or what—is responsible when something goes wrong. Under these conditions, identity has shifted from a “nice-to-have” feature to a foundational requirement. Some may ask why IP addresses or QR codes are not sufficient. These solutions can work within limited, closed systems, but they are poorly suited to serve as the foundational identity mechanism of a machine society. IP addresses depend on network connectivity and are inherently changeable. QR codes require line-of-sight scanning and human or camera intervention, which reduces reliability in industrial and harsh environments. RFID, by contrast, offers contactless identification, strong uniqueness, physical embeddability, and environmental robustness. In practical deployments, identity recognition is typically enabled by a combination of RFID chips and uhf rfid antenna systems, allowing machines to be identified reliably without physical contact or human participation. Within a robotic society, RFID is not merely a serial number—it is the physical root of a digital identity system. Each RFID chip carries a unique identifier that can be bound to a robot at manufacturing or during system onboarding. Even when a robot is offline, powered down, or partially disassembled, its identity remains intact. Around this physical anchor, backend systems build comprehensive mappings that link the RFID ID to model information, ownership, permission levels, operational s...

Human understanding of the deep sea still lags far behind our imagination of outer space. Although more than 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans, only a small fraction of deep-sea regions has been systematically explored and documented. As deep-sea resource development, marine scientific research, and polar exploration continue to accelerate, a critical challenge has emerged: how to reliably identify, track, and manage equipment and samples in an extreme subsea environment characterized by high pressure, low temperature, severe corrosion, and the absence of GPS signals. This is where RFID technology is beginning to play an increasingly important role in deep-sea operations. 1. The Information Blind Spots of Deep-Sea Operations In traditional deep-sea missions, whether involving ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles), AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles), or deep-sea landers and sampling tools, information management has largely relied on manual labeling, video review, and mission logs. These approaches suffer from several inherent limitations. First, real-time verification is difficult; errors in sample recovery are often discovered only after the equipment returns to the surface. Second, data linkage is weak—equipment IDs, samples, timestamps, and depth information are often stored separately, making it hard to establish a complete traceability chain. Third, during long-term or multi-expedition projects, equipment mix-ups and sample misidentification remain common risks. As deep-sea exploration moves toward larger-scale and more systematic operations, traditional manual methods are no longer sufficient. 2. Why RFID Is Well Suited for Deep-Sea Environments RFID was not originally designed for deep-sea applications, yet several of its inherent characteristics make it particularly suitable for subsea use. First, RFID does not rely on line-of-sight. Unlike QR codes or visual markers, RFID uses radio-frequency communication, enabling stable identification even in turbid water and low-light conditions. Second, RFID components can be robustly encapsulated. In deep-sea scenarios, antennas such as RFID ceramic antennas are especially valuable due to their excellent resistance to high pressure, saltwater corrosion, and long-term environmental stress. Third, RFID provides unique identification. Each tag carries a globally unique ID, effectively creating a “digital identity” for every piece of equipment or sample—an essential foundation for deep-sea data systems. For compact subsea instruments and sampling containers, small UHF RFID antennas can be embedded directly into housings without affecting mechanical integrity, enabling identification while preserving streamlined structural design. In underwater applications, RFID is typically deployed for short-range identification, often operating in coordination with underwater communication systems rather than attempting long-distance wireless transmission. 3. Intelligent Identification and Management of...

Behind the frequently mentioned phrase “the brain-inspired era” lies a profound paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence is no longer driven only by bigger models and more computing power, but is beginning to learn from the human brain itself: perception, association, memory, decision-making, and evolution. Models are becoming more like a “digital brain.” Yet a fundamental question emerges: how can such a brain truly understand the real world? Without perceptual gateways, even the most powerful neural network is merely an “island of intelligence” trapped inside data. In this context, RFID is quietly becoming the first critical bridge connecting the physical world with brain-inspired intelligence. Traditional AI mainly learns from text, images, and speech on the internet — a “described world.” But true brain-inspired intelligence needs a “perceived world.” Just as a baby does not learn by reading books, but by touching, grasping, and observing, machines must build cognition through direct interaction with reality. UHF RFID tags — including specialized forms such as UHF RFID sport tags — act as the “sensory neurons” of this system, giving every object a unique, readable digital identity. When billions of items become perceptible, the world itself turns into a living perceptual map for neural networks. Technically, RFID is far more than an advanced barcode. It is a neural encoder for the physical world. RFID ceramic antennas enable stable and reliable sensing in harsh environments such as metal surfaces, high temperatures, and industrial workshops, while long-range and directional reader architectures provide spatial perception similar to human vision. A long range RFID reader module combined with a directional RFID reader gives the system “far-sight” and “focus,” allowing machines to understand where objects are, how they move, and how they interact in space — exactly like a visual cortex for the industrial world. In brain-inspired systems, perception is never isolated. It is tightly coupled with memory, reasoning, and prediction. RFID’s unique strength lies in its built-in time dimension and causal traceability. From raw material to finished product, every lifecycle event is captured by UHF RFID, forming an “experience memory” for neural networks. When an anomaly occurs, the system recalls similar sensory histories and predicts failure paths, making decisions closer to human intuition. In manufacturing, this bridge is already transforming factories. Traditional digital plants rely on dashboards; brain-inspired factories rely on perception. RFID-enabled machines, tools, and materials become part of a living sensory network. With ceramic-antenna-based tags surviving harsh production lines and long-range readers covering wide shop-floor areas, neural networks learn process laws, quality causality, and hidden risk patterns. The factory evolves from automation to cognition. In logistics and smart cities, the same architecture scales into a “sensory nerv...

In life sciences, medical diagnostics, and biopharmaceutical research, laboratories are no longer defined solely by test tubes and microscopes. As testing volumes grow, sample types diversify, and regulatory requirements become increasingly stringent, traditional laboratory management models—largely dependent on manual records and barcode-based identification—are revealing clear limitations. Issues such as low efficiency, high error rates, and insufficient traceability have become difficult to ignore. Against this backdrop, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is emerging as a foundational enabler of laboratory automation and digital transformation, particularly in the end-to-end management of biological samples. Challenges in Biological Sample Management Biological samples are highly sensitive and often irreplaceable. Whether dealing with blood, tissue sections, DNA samples, or cell cultures, any mix-up, contamination, or loss can compromise experimental results, derail research projects, or even lead to regulatory violations. In hospital laboratories, biobanks, and third-party testing facilities, thousands of samples may circulate daily, passing through tightly coupled stages such as collection, aliquoting, testing, storage, and transportation. While barcode systems have improved basic identification, they still rely heavily on manual scanning and visual confirmation. Labels can easily degrade under chemical exposure or ultra-low temperatures. In contrast, UHF RFID stickers designed for laboratory use can be securely attached to sample tubes and cryogenic containers, maintaining stable performance throughout high-throughput workflows and harsh storage conditions. RFID as the Foundation of Laboratory Automation Compared with barcodes, RFID offers significant advantages, including contactless operation, bulk reading capabilities, and stronger adaptability to harsh environments. By embedding RFID tags into sample tubes, cryoboxes, or transport trays, laboratories can identify and track samples without opening containers or performing individual scans. Within an automated laboratory ecosystem, RFID is more than a simple identification tool—it acts as a critical link connecting samples, equipment, and information systems. Industrial-grade RFID readers deployed at workstations, storage entrances, and transfer points ensure stable and accurate data capture even in electromagnetically complex laboratory environments. When integrated with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), automated aliquoting instruments, and cold-chain storage systems, RFID enables a sample-centric data network. Samples are automatically logged, verified, and tracked as they move through each process, significantly reducing reliance on manual intervention. End-to-End RFID Applications in Sample Workflows At the sample collection stage, RFID tags can be assigned and bound to sample data at the point of origin, minimizing the risks associated with delayed or m...
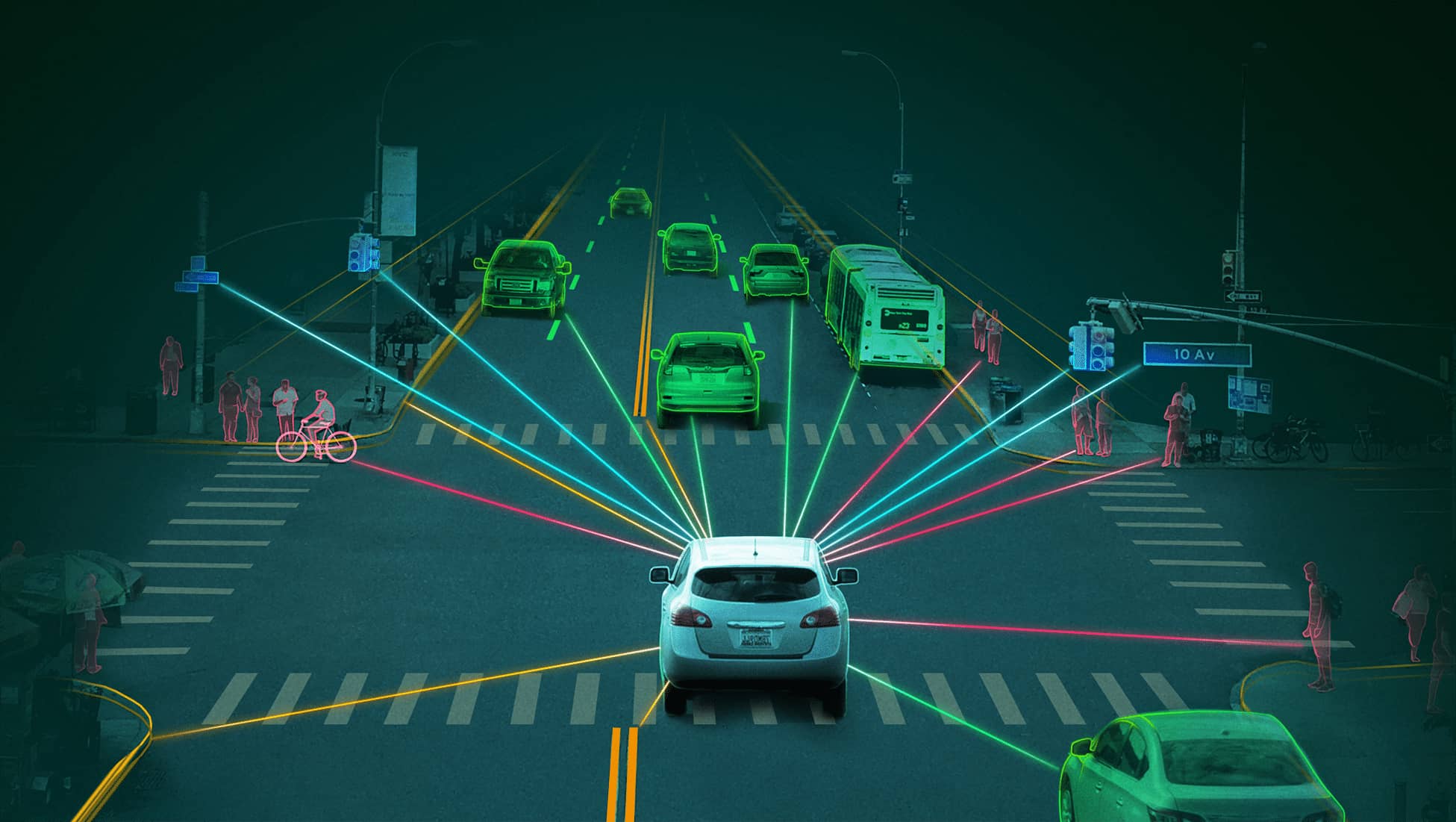
The progress of autonomous driving is often described as a competition in algorithms, computing power, and sensors. In reality, it is increasingly becoming a systems challenge—one that depends on how effectively vehicles and roads can work together. Relying solely on cameras, millimeter-wave radar, or LiDAR still leaves autonomous vehicles vulnerable to unstable recognition, environmental interference, and high system redundancy costs. Against this backdrop, RFID technology is being re-evaluated, gradually moving from logistics and manufacturing into intelligent road infrastructure and RFID vehicle management systems. From “Seeing” the Road to “Understanding” It Most autonomous vehicles today interpret road conditions through visual and radar-based perception. Lane markings, traffic signs, signals, and obstacles are detected passively, based on what sensors can observe at a given moment. Under ideal conditions, this works well. However, rain, snow, fog, glare, worn lane markings, or temporary construction zones quickly expose the limits of this approach. The road itself remains silent, offering no direct confirmation of what a vehicle believes it sees. RFID markers change this relationship. By embedding RFID tags into key road elements—lanes, intersections, speed-control zones, construction areas, and roadside infrastructure—the road gains a digital identity that can be read directly by vehicles. With properly designed UHF RFID antennas installed on vehicles or embedded near the roadway, information can be captured reliably without dependence on visibility or lighting conditions. How RFID Is Deployed in Intelligent Road Systems In road environments, RFID typically takes the form of passive UHF tags or ruggedized, weather-resistant markers installed beneath the road surface, along curbs, within guardrails, or inside traffic facilities. Autonomous vehicles equipped with onboard RFID readers can automatically detect these markers as they pass, without any active interaction. To support stable reading at driving speeds, vehicles often integrate a long-range RFID reader module, allowing tags to be identified early enough for decision-making. Each tag can store standardized information such as road classification, speed limits, lane attributes, intersection identifiers, or warnings related to temporary conditions. When integrated with high-definition maps and vehicle control systems, RFID enables vehicles to anticipate road conditions rather than react to them. Enhancing Positioning Accuracy Where GPS Falls Short High-precision positioning remains one of the most difficult challenges in autonomous driving. Even when combining GNSS, inertial measurement units, and visual SLAM, location drift can occur in tunnels, dense urban areas, or locations with poor satellite coverage. RFID markers provide fixed physical reference points. Each time a vehicle reads a tag, it can recalibrate its position with high confidence. This approach has proven particularly val...
Categories
New Products
JT-6210 0-1m UHF RFID Desktop USB Reader Writer ISO18000-6C Read More
JT-7100 0-3m 860-960MHz UHF RFID Industrial Grade RFID Reader Read More
JT-8380 0-6m UHF RFID 860-960MHz Middle Range Integrated Reader Read More
JT-P983 Industrial Tablet Pad RFID Handheld Reader Grade Long Range Android UHF Terminal Bluetooth RFID Reader For Warehouse Read More
JT-1550 Small Mini HF RFID 13.56MHz Module ISO14443A ISO 15693 Protocol Read More
JT-2302A 13.56MHz RFID Module ISO14443A ISO15693 Protocol Read More
JT-2302 HF RFID 13.56MHz Module ISO14443A ISO15693 Support Mifare1 IC card Read More
JT-2540 TM200 UHF RFID 4-port Module 860-960MHz TTL Read More
Copyright © 2026 Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

IPv6 network supported