 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
 Call at :
+86 18681515767
Call at :
+86 18681515767
 Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
Email :
marketing@jtspeedwork.com
1. Design & Structure Differences Anti-Metal Tags → Equipped with wave-absorbing materials (e.g., ferrite layers) or metal isolation layers—like wearing "EMI armor." → Often have foam adhesive or rigid casings to avoid direct contact with metal surfaces. Regular Tags → No anti-metal design. Placing them on metal surfaces causes signal failure, similar to a phone losing signal in a shielded room. 2. Application Scenarios Scenario Anti-Metal Tags Regular Tags Metal Surfaces ✅ Machinery, tool cabinets, car parts ❌ Unreadable on metal Harsh Environments ✅ High humidity, extreme temperatures ✅ Only for mild conditions Non-Metal Surfaces Works but overkill (higher cost) ✅ Ideal for cardboard, plastic, etc. 3. Performance Comparison Feature Anti-Metal Tags Regular Tags Read Range 3–10 meters on metal surfaces Nearly unreadable on metal Signal Stability Resists interference from metal reflections Easily disrupted by metal Cost Higher (due to specialized materials) Lower 4. Technical Principle Why Regular Tags Fail on Metal Metal reflects electromagnetic waves, causing two issues: Energy Loss: The tag’s antenna can’t harvest enough power from the reader. Signal Noise: Reflected waves interfere with the reader’s signals. How Anti-Metal Tags Overcome This Isolation Layer: Absorbs or blocks reflected waves (e.g., foam spacers or magnetic layers). Tuned Antennas: Optimized for metal’s dielectric properties to maintain resonance at UHF frequencies (860–960 MHz). Ground Plane Effect: Uses the metal surface as part of the antenna to boost signal range. 5. Real-World Use Cases Anti-Metal Tags Healthcare: Track surgical tools during sterilization (high-temperature-resistant tags). Automotive: Monitor metal parts on assembly lines (ceramic tags withstand 200°C). Energy: Monitor pipelines or transformers (corrosion-resistant tags). Regular Tags Retail: Track clothing or cardboard packaging. Logistics: Label plastic pallets or containers. Key Analogy Regular Tags = A radio in a metal room (signals get blocked). Anti-Metal Tags = A satellite phone that penetrates interference.
Introduction: UHF RFID gate readers have emerged as indispensable devices in various industries, revolutionizing the way data is captured and processed. This article explores the significance of UHF gate readers, their price considerations, and their ability to handle multiple tags simultaneously. UHF RFID Gate Readers: UHF gate readers utilize radio frequency technology to identify and track RFID tags. They are designed to capture real-time data as objects or individuals pass through gateways or portals. Unlike traditional barcodes, UHF gate readers enable contactless scanning, allowing for the simultaneous detection of multiple tags within their read range. Price Considerations: When considering the price of UHF RFID gate readers, various factors come into play. These factors include the reader's features, read range, additional functionalities, and the supplier's pricing structure. Organizations should carefully assess their specific requirements and budget constraints before making a purchase. Comparing prices from different suppliers and conducting thorough research can help identify a cost-effective solution that meets their needs. The Importance of UHF RFID Gate Readers: UHF gate readers offer several advantages across industries. With their ability to read multiple tags quickly and accurately, these readers enhance operational efficiency. The wide reading range of UHF gate readers ensures reliable tag detection, even in challenging environments. This makes them ideal for applications such as access control, inventory management, supply chain optimization, and asset tracking. Unleashing the Power of Multiple Tag Handling: One of the standout features of UHF gate readers is their capability to handle multiple tags simultaneously. This enables rapid and efficient data capture, significantly reducing the time and human effort required for scanning individual tags. By streamlining processes, UHF gate readers enhance productivity, reduce potential errors, and provide real-time insights for better decision-making. Identifying the Best RFID Reader: Choosing the best RFID reader requires careful consideration. Key factors to assess include functionality, reliability, and performance. Organizations should seek out readers that prioritize advanced technology, accuracy, and seamless integration capabilities. Prioritizing these factors ensures optimal performance and a seamless integration with existing systems. Conclusion: UHF RFID gate readers have become vital tools in capturing and processing data efficiently. Their contactless, simultaneous scanning of multiple tags sets them apart from traditional barcode systems. With careful consideration of pricing, organizations can find a cost-effective solution that meets their specific needs. UHF gate readers offer numerous benefits, including improved operational efficiency, accurate data capture, and real-time insights. By selecting the best RFID reader, organizations can unleash the power of multiple t...
In today's advanced technology-driven world, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) systems have become integral to various industries, revolutionizing access control and inventory management processes. Among the diverse range of RFID solutions available, UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) gate readers have gained prominence for their ability to efficiently read multiple tags simultaneously. This article explores the significance of UHF RFID gate readers, their benefits, pricing considerations, and a few notable manufacturers. UHF gate readers serve as powerful tools for access control and inventory management systems. They employ radio frequency transmissions to identify and track RFID tags attached to objects, assets, or individuals. These gate readers are specifically designed to capture and process tag data in real time as items pass through a gate or portal. Unlike traditional barcode systems requiring line-of-sight scanning, UHF RFID gate readers enable contactless and simultaneous scanning of multiple tags within their read range. One key advantage of UHF gate readers is their ability to read multiple tags quickly and accurately, enhancing operational efficiency. With a wide reading range typically spanning several meters, UHF gate readers offer seamless and reliable detection of RFID tags, even in dynamic and crowded environments. This makes them ideal for various applications such as access control, inventory management, supply chain logistics, and asset tracking. Pricing is an important consideration when selecting UHF RFID gate readers. Prices can vary depending on factors such as the manufacturer, features, read range, and additional functionalities. It is crucial for organizations to evaluate their specific requirements and budgetary constraints before investing in a system. Conducting thorough research and contacting multiple suppliers will help in comparing prices and selecting the most cost-effective solution that meets the desired functionalities and performance criteria. UHF RFID gate readers provide organizations with enhanced control, visibility, and automation in their access control and inventory management processes. By investing in reliable gate readers from trusted manufacturers, businesses can streamline operations, improve accuracy, reduce manual efforts, mitigate losses, and optimize their overall efficiency. In conclusion, UHF RFID gate readers play a crucial role in revolutionizing access control and inventory management systems. With their ability to simultaneously read multiple tags, these gate readers enable efficient tracking and management of assets, products, and personnel. Considering factors such as pricing, manufacturer reputation, and specific requirements will assist organizations in selecting the best UHF gate reader solution that aligns with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Exploring New Frontiers for UHF RFID Modules in 2023 Introduction: UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) modules have been widely used in various industries for tracking and identification purposes. As we enter the year 2023, the opportunities for UHF RFID modules are set to expand even further. In this article, we will delve into the potential areas where UHF RFID modules can find new applications and contribute to technological advancements. 1. Supply Chain and Inventory Management: One significant opportunity lies in the optimization of supply chain and inventory management. UHF RFID modules can revolutionize the way businesses track and monitor their products. With the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously over long distances, these modules can enhance inventory accuracy, reduce stockouts, and streamline logistics processes. The real-time visibility provided by UHF RFID modules enables retailers and manufacturers to improve efficiency and meet customer demands more effectively. 2. Retail and Customer Engagement: In the retail sector, UHF RFID modules offer exciting possibilities for enhancing customer experiences. By embedding tags in products, retailers can create interactive shopping experiences. Customers can simply wave a product past an RFID reader to access detailed information, reviews, or promotional offers. This technology opens avenues for personalized marketing and tailored recommendations, helping retailers strengthen customer engagement and loyalty. 3. Smart Cities and Asset Tracking: UHF RFID modules can play a vital role in the development of smart cities by simplifying asset tracking. By integrating RFID technology with municipal infrastructure, cities can efficiently manage public resources such as vehicles, equipment, and shared amenities. UHF RFID modules can provide real-time data on asset location, maintenance requirements, and usage patterns, enabling better resource allocation, cost savings, and improved service delivery. 4. Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Industry: The healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors can also benefit greatly from UHF RFID modules. These modules can enhance patient safety, medication tracking, and supply chain integrity. With UHF RFID-enabled medication bottles and tags on medical equipment, hospitals can automate inventory management and monitor patient medication adherence more effectively. Additionally, in the pharmaceutical industry, UHF RFID modules can help combat counterfeit drugs by ensuring product authentication throughout the supply chain. 5. Security and Access Control: Another area where UHF RFID modules offer promising opportunities is in security and access control systems. By integrating UHF RFID technology into identification cards or access badges, organizations can streamline entry processes, enhance security protocols, and track employee movements within facilities. This technology can also be applied to event management, ticketing systems, and v...
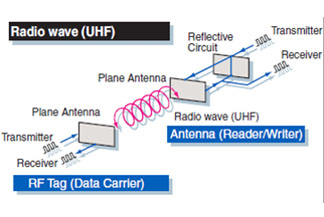
Basic Characteristics of Radio Frequency Propagation Attenuation What cannot be avoided in RF propagation is attenuation. Literally, attenuation is to reduce the strength of the RF signal. To be precise: when the signal propagates in the transmission medium, a part of the energy will be converted into heat energy or absorbed by the transmission medium, resulting in the continuous weakening of the signal strength. This phenomenon is called attenuation. The phenomenon that the signal of the UHF RFID reader decreases in amplitude after passing through the water medium is attenuation. The general attenuation is represented by L (Loss): Among them, Po represents the power before attenuation; Pi represents the power after attenuation. L is negative in dB under attenuation and Po is less than Pi Attenuation in RF propagation exists in the following places: In the cable—The resistance between the cable and the connector converts RF into heat. The energy expansion caused by the path in the air is the biggest factor of failure, and dust, rain and fog in the air will cause failure. Passive components in the system heat up, causing the RF signal to fail. Artificially added to the system to reduce the sincerity (useful). It should be emphasized that attenuation wells are not necessarily a bad thing. In many cases, attenuation is performed at the front end of the circuit in order to protect the circuit, or attenuation is performed before the antenna output in order to control the radiation range, all of which are positive for the entire system thing. Gain 1) RF gain Gain is the opposite of attenuation, resulting in increased RF signal strength. RF gain (not antenna gain) is generated by active devices. It can be understood that to amplify a signal, it must be given corresponding energy. Generally, gain is expressed as Gain: Among them, Po represents the output power, and Pi represents the input power. Gain's dB is negative for attenuation and Po is less than Pi: Gain's dB is positive for gain and Po is greater than Pi. If a positive gain is achieved, external energy needs to be introduced and supplied to the amplifying device to achieve signal amplification. Below Figure is a schematic diagram of attenuation and gain, where the signal is attenuated by passive devices to reduce amplitude and generate heat loss; the amplitude is enhanced by the energy gain provided by active devices. One thing to note is that the operating frequency of the signal remains the same regardless of gain or attenuation. 2) Antenna gain When it comes to antenna gain, it needs to be distinguished from RF gain, which is completely different from RF transmission gain. The gain of an antenna is to increase the intensity of energy in a particular direction rather than to increase its total energy. Antennas are generally passive components and cannot provide additional energy to enhance the RF signal. Below Figure is a schematic diagram of the radiation of a pot-shaped microwave antenna. The...
Three Minutes to Take You to Understand RFID Technology RFID technology actually refers to radio frequency technology. Its technology mainly relies on the principle of magnetic field or electromagnetic field to realize two-way communication between devices through radio frequency, so as to realize the function of exchanging data. The biggest feature of this technology is that it can obtain each other without contact. RFID information, ETC, logistics, and libraries are several typical application scenarios. The commonly used radio wave frequency bands for RFID technology mainly include: low frequency, high frequency, ultra-high frequency and microwave frequency bands.RFID system compositionRFID system is mainly composed of three parts: reader, electronic label and data management system. RFID Reader: Also known as a reader , it is mainly used to read out the information in the electronic tag, or write the information required by the tag into the tag. According to different uses, readers are divided into read-only readers and read/write readers, which are the information control and processing center of the RFID system. When the RFID system works, the reader transmits radio frequency energy in an area to form an electromagnetic field, and the size of the area depends on the transmission power. The tags in the coverage area of the reader are triggered, send the data stored in it, or modify the data stored in it according to the instructions of the reader and can communicate with the computer network through the interface . RFID Tag: The electronic tag is mainly used to store certain data information. At the same time, it will accept the signal from the reader and send the required data back to the reader. The electronic tag is generally attached or fixed to the on the item. Data management system: The main work is to process the electronic tag data transmitted by the reader for analysis, and at the same time complete the functions required by the user. For example, the following system flow: How RFID systems work When the rfid tag is within the recognition range of the reader, the reader emits radio wave energy of a specific frequency, and the electronic tag will receive the radio frequency signal sent by the reader and generate an induced current. Using the energy generated by this current, the electronic tag sends out the information stored in its chip. Such electronic tags are generally referred to as passive tags or passive tags, or the tags actively send a signal of a certain frequency to the reader, and such electronic tags are generally referred to as active tags or active tags. After the reader receives the information returned by the electronic tag, it decodes it, and then sends it to the relevant application software or data management system for data processing. RFID classification RFID technology can be divided into three categories according to the power supply method of its tags, namely passive RFID, active RFID and semi-active RFID. 1...
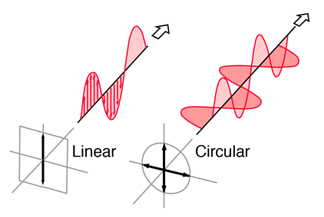
How To Select an RFID Antenna An RFID antenna is a necessary part of any RFID system. Unless the antenna is embedded into a reader, you will have to select and purchase the right antenna for your application. And there are a lot of options to select from. Frequency– this will depend on your tags – choose between LF, HF, UHF or Microwave frequency. Frequency Region– this will depend on country of operation and will affect only the UHF frequency. As you know, due to regulations, the frequency bands for UHF RFID slightly differ for US, Europe and other regions. Most UHF antennas are specified as globaland they are tuned for operation between 860 to 960 MHz. You can also find antennas that are specifically tuned for each region, which slightly improves their performance in the particular region. For instance, 865 - 868 MHz antenna will perform better when deployed in Europe than a global antenna, although this may not be distinguishable in most applications. Global antenna will work well for most applications; however, you can choose region-specific antenna for difficult deployments (long read ranges, RF challenging environment) or where global is not available. Read range and size– smaller antennas within the same frequency will have shorter read range and vice versa. The antennas with the shortest read range for UHF technology will be Near Field Antenna, that utilize near field as opposed to far field as regular UHF antennas. These are often used for item tracking and where short ranges are required for item singulation and/or security purposes. Profile width– if you are short on space or for esthetic reasons, you may need to look for low profile antennas that have a side connector or a side pigtail. Gain– gain affects read range and beamwidth. Antennas with higher gain will have longer read range but narrower beam. Antennas with lower gain will have shorter read range and wider beam width. Select antenna gain based on the shape of your interrogation zone and coverage needs. Most common gain is 6dBi but you can find antenna with 1 dBi (low gain) and also with 11 dBi (high gain). Polarization– you can select between circular and linear polarization. Circularly polarized antennas will have shorter read range but will be less orientation sensitive. You can select between right hand circularly polarized antennas (RHCP) or left hand circularly polarized antenna (LHCP). Sometimes you can see dual circularly polarized antennas that have both left hand and right hand polarization. Linearly polarized antennas will provide longer read range and more focused beam but will read only tags that have antennas parallel to the plane of wave. If your tag orientation is not fixed, especially when using single dipole tag antennas (which are most common), you should select a circularly polarized antenna. VSWR– voltage standing wave ratio or also called return loss - Due to mismatches in impedance within the connector, some of the signal is reflected. The ratio of the i...
Dual-frequency RFID is a relatively special application market. It is still relatively narrow and the industry chain is relatively simple. At present, the dual-frequency RFID chips on the market mainly use UHF+HF to make the same IC. There are still some scenarios in the market that use UHF. Tag + HF tag two different tags combined scheme. In addition to the chip threshold, dual-frequency tag equipment and manufacturing are also more difficult than ordinary tags, because the working principles of HF and UHF two different frequency bands are completely different, one is near-field coupling and the other is far-field radiation, which requires two different antenna combinations. In addition, the current usage of dual-frequency products is not large, so dual-frequency RFID products are more expensive than ordinary ones, whether they are chips or tags. According to the information we have investigated, the application volume and application scenarios of dual-frequency RFID tags are rapidly increasing, and may become a new market growth point. 1. Introduction to the advantages of dual-frequency RFID The advantages of dual-frequency RFID products are mainly in the following two aspects: >>Advantage 1: The function of UHF RFID for rapid inventory in large quantities is retained The biggest advantage of UHF RFID is that it has a long transmission distance and can be read in groups. It is very suitable for some scenarios that require quick inventory, especially in the B-side warehousing logistics and sorting links. >>Advantage 2: retains the ability of HF RFID to interact with mobile phones Because the NFC on the mobile phone is a kind of HF RFID technology, the HF RFID tag can interact directly with the mobile phone, which greatly expands the use boundary of RFID. Anti-counterfeiting traceability requirements. Therefore, dual-frequency RFID tag products can not only meet the needs of the B-side for efficient turnover, anti-lost, and visual management, but also meet the needs of the C-side crowd for anti-counterfeiting and traceability, which can form a good closed loop in business. 2. Dual frequency RFID market and application introduction The application scenarios of dual-frequency RFID products mainly have the following characteristics: The usage scenarios need to combine the high inventory efficiency of ultra-high frequency and the characteristics of high frequency interaction with mobile phones, which requires a relatively large amount of applications and concentrated, and then there is a demand for large-scale inventory; in addition, the consumption attributes of products are strong , need to interact directly with consumers. The unit price of the product in the application scenario is more expensive, because the product is more expensive, it will stimulate the consumer's need for anti-counterfeiting traceability. Only high-value scenarios can afford such a cost input. There is a strong demand for authenticity identification, but there is...
1
22
pagesCategories
New Products
JT-6210 0-1m UHF RFID Desktop USB Reader Writer ISO18000-6C Read More
JT-7100 0-3m 860-960MHz UHF RFID Industrial Grade RFID Reader Read More
JT-8380 0-6m UHF RFID 860-960MHz Middle Range Integrated Reader Read More
JT-P983 Industrial Tablet Pad RFID Handheld Reader Grade Long Range Android UHF Terminal Bluetooth RFID Reader For Warehouse Read More
JT-1550 Small Mini HF RFID 13.56MHz Module ISO14443A ISO 15693 Protocol Read More
JT-2302A 13.56MHz RFID Module ISO14443A ISO15693 Protocol Read More
JT-2302 HF RFID 13.56MHz Module ISO14443A ISO15693 Support Mifare1 IC card Read More
JT-2540 TM200 UHF RFID 4-port Module 860-960MHz TTL Read More
Copyright © 2026 Shenzhen Jietong Technology Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

IPv6 network supported